
EMC: It is the ability of a system or device to perform its functions (without an irreversible electromagnetic disturbance) without being affected by the electromagnetic environment it is in. A device should not emit unwanted electromagnetic waves that may affect other devices around it and at the same time should not be affected by unwanted waves emitted by other devices. One of the main factors determining EMC quality is the cables connecting the devices. Because, as they transmit unwanted electromagnetic waves from one point to another (interference through conductivity), they also spread the signals circulating on them like an antenna (interference by radiation). The two main factors that determine cable performance are the quality of the shielding material and the cable shielding grounding.
1-SCREENING
Shielding efficiency is calculated using the ratio of the signal received without the display to the signal received with the display. Using the data obtained from the measurement procedures with the mathematical formulations given in the table below, the shielding efficiency is calculated in different frequency ranges.
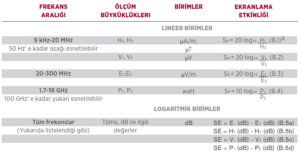
Magnetic field without H1 shielding (reference reading)
Magnetic field with H2 shielding
Voltage read when V1 is not shielded (reference reading)
Voltage read with V2 shielding
E1 electric field without shielding (reference reading)
Electric field with E2 shielding
Power without P1 shielding (reference reading)
Power with P2 shielding
The materials to be selected for shielding can be grouped into three groups:
1) High Performance Materials
100% coverage (80-120 dB shielding effectiveness) made of materials such as steel, copper, stainless steel
2) Standard Performance Materials
Conductive metal layers (20-40 dB shielding effectiveness)
3) Poor Performance Materials
Metallized fabric structures conductive paper materials (conductive polymers) (15-30 dB shielding efficiency)
In practice, 40 dB shielding efficiency can solve most problems.
100-120 dB shielding efficiency can be requested in military systems.
2-GROUNDING
An electrical circuit or device with a conductive interconnection, intentionally or unintentionally,
(to ground potential) or to a reference surface large enough to replace ground. Earth
absolute reference is considered zero volts. For a true grounding, all appliances must be brought to this kitchen zero point.
Some of the structures that can replace soil in practice:
-Steel lattice buildings
-Vehicle body (car, plane, ship)
-Water pipes
-Ground electrode systems
-Grounding plate and cage etc.
Since the cables are used in signal transmission between the source and the load, which side the shielding will be made and Grounding quality is very important. In a cable shielded only by the load, unwanted electric fields are well shielded. However, this is not enough to shield magnetic fields. When grounding is applied on both the load and source side, electric field shielding is better and magnetic shielding is also provided. (10-20 dB shielding efficiency increases) Magnetic leakage is reduced by using twisted pair conductors (reducing the area between the conductors and allowing opposite currents to flow by twisting). When grounding is applied from both sides electrical and magnetic shielding is effectively provided.
